Graphing on a Number Blood
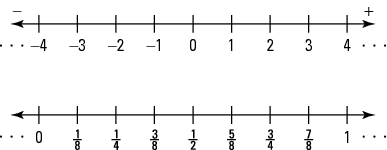
Integers and real numbers can be portrayed on a number line. The point connected this line associated with each number is titled the graph of the list. Notice that number lines are leaded equally, or proportionately (figure Figure 1).
Figure out 1. Number lines.
Graphing inequalities
When graphing inequalities involving only integers, dots are used.
Example 1
Graph the set of x much that 1 ≤ x ≤ 4 and x is an integer (see Figure 2).
{ x:1 ≤ x ≤ 4, x is an whole number}

When graphing inequalities involving real numbers, lines, rays, and dots are used. A dot is used if the number is enclosed. A hollow dot is used if the number is not included.
Example 2
Graph as indicated (see Figure 3).
-
Graph the go under of x such that x ≥ 1.
{ x: x ≥ 1}
-
Graph the set of x such that x > 1 (see Chassis 4).
{ x: x > 1}
-
Graphical record the set of x so much that x < 4 (see Figure 5).
{ x: x < 4}
This ray is a great deal called an open shaft or a incomplete line. The hollow DoT distinguishes an open ray from a ray.



Intervals
An interval consists of all the numbers that belong within two certain boundaries. If the two boundaries, Beaver State rigid numbers, are included, then the interval is called a closed interval. If the fixed numbers are non included, then the interval is called an open interval.
Example 3
Graph.
-
Closed musical interval (see Figure 6).
{ x: –1 ≤ x ≤ 2}
-
Open interval (see Figure 7).
{ x: –2 < x < 2}


If the interval includes only one of the boundaries, then it is known as a half‐open separation.
Example 4
Graph the half‐open interval (find out Figure 8).
{ x: –1 < x ≤ 2}

how to graph x 2 on a number line
Source: https://www.cliffsnotes.com/study-guides/algebra/algebra-i/inequalities-graphing-and-absolute-value/graphing-on-a-number-line

0 Komentar