Solutions, examples, videos, worksheets, and activities to aid Algebra II students get wind about arithmetic sequences.
The following figure gives the convention to find the nth term of an arithmetic successiveness. Scroll toss off the page for more examples and solutions.
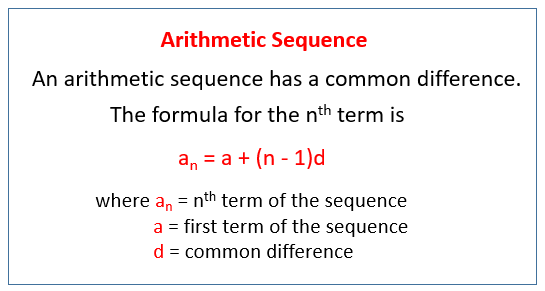
Arithmetic Sequences
A list of numbers that follows a rule is known as a sequence. Sequences whose formula is the addition of a constant are called arithmetic sequences, analogous to geometric sequences that follow a formula of generation. Homework problems on arithmetical sequences often ask us to find the nth term of a sequence using a formula. Arithmetic sequences are momentous to agreement arithmetical serial.
How to see the general condition of an arithmetic sequence?
- Show Step-by-step Solutions
Introduction to arithmetical sequences
Determine the n-th term of an arithmetic sequence.
Determine the common difference of an arithmetic sequence.
Determine the formula for an pure mathematics sequence.
An arithmetic chronological succession is a sequence that has the pattern of adding a constant to determine consecutive price. We say arithmetical sequences take up a common difference.
Examples:
- A sequence is a function. What is the sphere and range of the pursuit chronological succession?
9,6,3,0,-3,-6
- Given the formula for the arithmetic chronological succession, determine the kickoff 3 damage and so the 8th term. Also posit the shared difference.
an = -4n + 3
- Given the arithmetic sequence, determine the formula and the 12th term.
-2,1.5,5,8.5,12,15.5, …
- Show Piecemeal Solutions
Quick Introduction to Pure mathematics Sequences
What an arithmetic sequence is with a few examples.
An arithmetic sequence is a episode where in line terms in the episode differ by a constant amount.
Illustration:
Determine which of the pursuit sequences are arithmetic. If they are arithmetical, give the value of 'd'.
3,8,13,18,23,28,33, …
-.7, -1.7, -2.7, -3.7, -4.7, …
1.6,2.2,2.8,3.3,3.9,4.5, …
4/3,5/3,2,7/3,8/3,3, …
- Show Whole step-by-step Solutions
Pure mathematics Sequences and Partial Sums
An arithmetic sequence may be thought of as a linear function whose domain is the unmoving of natural numbers.
an = dn + c
The y-stop is not the first term of the sequence.
c = a1 - d
a0 = dn + a1 - d
Examples:
- Find a formula for the n-th term of the arithmetic sequence whose coarse difference is 3 and whose basic term is 2.
- The fourth term of an arithmetic sequence is 20, and the 13th term is 65. Write the early 6 terms of the episode.
- Find the 9th term of the arithmetic sequence that begins with 2 and 9.
- Find the meat of the first 9 natural Numbers.
- Pentad the union of the mortal arithmetic sequence
1+3+5+7+9+11+13+15+17+19
- Find the sum of integers from
a) 1 to 100
b) 1 to N
- Find the sum of the first 150 terms of the sequence 5,16,27,38,49, …
- Show Step-by-step Solutions
Arithmetic Sequence
Example:
Find the common difference and the term named in the problem in the following arithmetic sequence.
-16, -18, -20, -22, …
- Show Step-by-step Solutions
Sample the free Mathway calculator and problem convergent thinker below to practice single math topics. Essay the given examples, or type in your own job and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this place Oregon page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback Page.
is 1 2 4 7 11 an arithmetic sequence
Source: https://www.onlinemathlearning.com/arithmetic-sequences.html

0 Komentar